The Role of Biodiversity in Eco-Friendly Gardening
In today’s fast-paced world, where urbanization and climate change are reshaping our landscapes, embracing biodiversity in gardening has never been more crucial. Imagine stepping into a garden where every plant, insect, and microbe plays a role in creating a vibrant ecosystem. This is not just a dream; it’s the reality that biodiversity brings to eco-friendly gardening. By promoting a variety of life forms, we can enhance sustainability, resilience, and ecological balance in our gardens. So, how does biodiversity contribute to these goals? Let’s dive in!
Understanding biodiversity is like unlocking a treasure chest of ecological benefits. It encompasses the variety of life forms—plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms—that contribute to the health and productivity of ecosystems. Think of biodiversity as the backbone of your garden; without it, everything becomes fragile and susceptible to challenges like pests, diseases, and climate fluctuations. A garden rich in biodiversity not only looks stunning but also supports sustainable practices, allowing nature to thrive alongside our gardening efforts.
When you incorporate diverse plant species into your garden, you’re not just adding color and texture; you’re creating a thriving ecosystem that offers numerous benefits. For instance, a varied plant palette can lead to improved soil health, natural pest control, and enhanced pollination. Here’s how:
Diverse plant species significantly contribute to healthier soil by enhancing nutrient cycling and organic matter. Different plants have unique root structures that interact in ways that benefit nutrient uptake and soil aeration. For example, deep-rooted plants can break up compacted soil, allowing air and water to penetrate more easily. This interaction promotes a healthier underground ecosystem, making your garden more resilient to drought and disease.
When various root systems coexist, they engage in a dance of nutrient exchange and soil aeration. This synergy not only improves the overall health of the soil but also encourages beneficial microbes and fungi to flourish. These microorganisms play a vital role in breaking down organic matter, releasing nutrients that plants can absorb. It’s like having a team of tiny helpers working tirelessly beneath the surface!
Plants contribute organic matter through litter and root decay, enriching the soil. As leaves fall and decompose, they provide a feast for earthworms and other soil organisms, which in turn improve soil structure and fertility. This cycle of life is essential for maintaining soil biodiversity, which directly impacts plant growth and health. A garden rich in organic matter is a garden that thrives.
One of the most exciting aspects of biodiversity is its ability to naturally regulate pests. A diverse garden ecosystem can reduce the need for chemical pesticides by fostering a balance between pests and their natural predators. For instance, planting a variety of flowering plants can attract beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings, which feast on aphids and other harmful pests. It’s nature’s way of keeping things in check!
Another vital role of biodiversity in eco-friendly gardening is its impact on pollinators. By planting a variety of flowering species, you can attract different pollinators essential for plant reproduction. This is particularly important as many pollinator populations are declining due to habitat loss and pesticide use. So, how can you make your garden a haven for these crucial creatures?
Using native plants can significantly enhance pollinator populations. Native flora has co-evolved with local pollinators, making them the perfect match. For example, native wildflowers can provide nectar and pollen, while their unique shapes may be specifically suited to certain pollinator species. This relationship is a beautiful example of how biodiversity supports ecological balance.
Designing gardens with diverse habitats supports various pollinators. Consider incorporating features like:
- Flowering plants that bloom at different times of the year
- Water sources like birdbaths or shallow dishes
- Undisturbed areas for nesting
These elements create inviting environments for bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects, ensuring your garden is buzzing with life!
Biodiversity also plays a crucial role in water conservation. By carefully selecting and arranging plants, you can improve water retention and reduce irrigation needs. For instance, grouping plants with similar water requirements can create microclimates that help maintain moisture levels.
Incorporating drought-resistant species can significantly lower water usage. These plants are adapted to survive in low-water conditions, making them ideal for eco-friendly gardens. Think of them as the superheroes of your garden, thriving even when the going gets tough!
Different plants contribute to better soil moisture retention. For example, ground covers can help shade the soil, reducing evaporation, while deeper-rooted plants can tap into moisture reserves below the surface. This diversity ensures that your garden remains lush and vibrant, even during dry spells.
Q: What is biodiversity in gardening?
A: Biodiversity in gardening refers to the variety of life forms, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, that contribute to a healthy and productive ecosystem.
Q: How does biodiversity improve soil health?
A: Diverse plants enhance nutrient cycling and organic matter, leading to improved soil structure and fertility.
Q: Why are pollinators important in gardening?
A: Pollinators are essential for plant reproduction, and their presence increases the yield and health of flowering plants.
Q: Can I create a biodiverse garden in a small space?
A: Absolutely! You can incorporate a variety of plants, flowers, and habitats even in small gardens or containers.

The Importance of Biodiversity
This article explores how biodiversity enhances eco-friendly gardening practices, promoting sustainability, resilience, and ecological balance. Discover the benefits, strategies, and various elements that contribute to a thriving garden ecosystem.
Understanding biodiversity is crucial for eco-friendly gardening. It encompasses the variety of life forms that contribute to ecosystem health, resilience, and productivity. Imagine your garden as a vibrant tapestry, where each thread represents a different species—plants, insects, birds, and even microorganisms—all working together to create a harmonious environment. This intricate web of life supports sustainable practices and enhances the beauty of gardens, making them not just visually appealing but also ecologically significant.
Biodiversity plays a pivotal role in maintaining ecological balance. For instance, when various species coexist, they create a natural equilibrium that can fend off diseases and pests, reducing the need for chemical interventions. This balance is akin to a well-rehearsed orchestra, where each musician contributes to a beautiful symphony. Without one instrument, the music would be incomplete, just as a garden lacking diversity may struggle to thrive.
Moreover, diverse ecosystems are more resilient to changes and stresses, such as climate fluctuations or pest invasions. Think of biodiversity as a safety net; it provides stability and insurance against unforeseen challenges. When one species faces a decline, others can fill the gap, ensuring the ecosystem continues to function smoothly. This resilience is essential for sustainable gardening practices, as it allows gardens to adapt and flourish over time.
Incorporating biodiversity into your garden can take many forms. You can introduce a mix of native and non-native plants, create habitats for various wildlife, and even cultivate a range of soil organisms. Each of these elements contributes to a robust ecosystem. For example, planting a variety of flowers not only beautifies your space but also attracts beneficial insects, which in turn help with pollination and pest control.
In summary, the importance of biodiversity in eco-friendly gardening cannot be overstated. It supports ecological balance, enhances resilience, and promotes sustainability. By embracing the variety of life forms in your garden, you're not just creating a beautiful space; you're also contributing to the health of the planet. So, why not start weaving that vibrant tapestry today?
Incorporating diverse plant species in your garden can lead to improved soil health, pest control, and pollination. This section discusses the specific advantages of using a variety of plants in eco-friendly gardening.
Diverse plant species contribute to healthier soil by enhancing nutrient cycling and organic matter. This section examines how a variety of roots and plant types can improve soil structure and fertility.
Different root systems interact in ways that benefit nutrient uptake and soil aeration. This subheading delves into how these interactions promote a healthier underground ecosystem.
Plants contribute organic matter through litter and root decay, enriching the soil. This section explains how diverse plants enhance soil biodiversity and overall health.
Biodiversity can naturally regulate pests through predation and competition. This section highlights how a diverse garden ecosystem can reduce the need for chemical pesticides.
Planting a variety of flowering species attracts different pollinators, which are essential for plant reproduction. This section discusses the importance of pollinator-friendly plants in eco-friendly gardening.
Using native plants can significantly enhance pollinator populations. This subheading explores the relationship between native flora and local pollinator species.
Designing gardens with diverse habitats supports various pollinators. This section outlines strategies for creating inviting environments for bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects.
Biodiversity can aid in water conservation through plant selection and arrangement. This section discusses how diverse plantings can improve water retention and reduce irrigation needs.
Incorporating drought-resistant species can significantly lower water usage. This subheading explores the benefits of selecting plants that thrive in low-water conditions.
Different plants contribute to better soil moisture retention. This section explains how a diverse garden can help maintain optimal moisture levels, reducing the need for frequent watering.
- What is biodiversity? Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms in a particular habitat, including plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- How does biodiversity benefit my garden? It enhances soil health, improves pest control, and attracts pollinators, making your garden more resilient and productive.
- Can I create a biodiverse garden in a small space? Absolutely! You can incorporate a variety of plants, flowers, and habitats even in small gardens or balconies.
- What are some examples of native plants I can use? Native plants vary by region, but examples include coneflowers, black-eyed Susans, and milkweed.

Benefits of Diverse Plant Species
Incorporating a variety of plant species into your garden isn't just about aesthetics; it plays a vital role in creating a thriving ecosystem. Think of your garden as a small community where different plants interact with each other, just like people in a neighborhood. Each plant species brings unique characteristics and benefits that contribute to the overall health and resilience of your garden. By embracing diversity, you're not only enhancing the beauty of your space but also promoting sustainability and ecological balance.
One of the most significant advantages of diverse plant species is the improvement of soil health. Different plants have varying root structures and nutrient needs, which can lead to enhanced nutrient cycling. For instance, deep-rooted plants can break up compacted soil layers, allowing for better aeration and water penetration. Meanwhile, shallow-rooted plants can help hold the topsoil in place, preventing erosion. When these plants coexist, they create a harmonious underground network that supports a rich soil ecosystem.
Additionally, a diverse plant community can significantly boost pest control efforts in your garden. When you have various species growing together, you create a complex habitat that attracts beneficial insects. These natural predators can help keep pest populations in check, reducing the need for harmful chemical pesticides. For example, ladybugs and lacewings thrive in diverse environments, and they feast on aphids and other garden pests. By fostering an ecosystem where these helpful creatures can thrive, you're promoting a healthier garden overall.
Moreover, diverse plantings encourage pollination, which is crucial for the reproduction of many flowering plants. Different species bloom at various times throughout the growing season, providing a continuous food source for pollinators like bees and butterflies. By planting a range of flowers with staggered blooming periods, you can create a vibrant garden that attracts these essential creatures. Not only do they help with pollination, but they also contribute to the overall biodiversity of your garden, making it a more resilient ecosystem.
To summarize, the benefits of incorporating diverse plant species in your eco-friendly garden include:
- Improved soil health through varied root structures.
- Natural pest control by attracting beneficial insects.
- Enhanced pollination from a variety of flowering plants.
By understanding these benefits, you can make informed choices about the plants you include in your garden. Not only will you create a visually stunning space, but you'll also contribute to a healthier environment. So, why not get started on your journey towards a more biodiverse garden today?
Q1: What are the best plants to include for biodiversity?
A1: Native plants are often the best choice as they are adapted to local conditions and support local wildlife. Additionally, consider including a mix of flowering plants, shrubs, and trees.
Q2: How can I attract more pollinators to my garden?
A2: Plant a variety of flowering species that bloom at different times of the year. Incorporating native plants and avoiding pesticides will also create a welcoming environment for pollinators.
Q3: Is it necessary to have a diverse garden?
A3: While it's not mandatory, a diverse garden is more resilient to pests, diseases, and environmental changes. It also supports a wider range of wildlife, contributing to ecological balance.
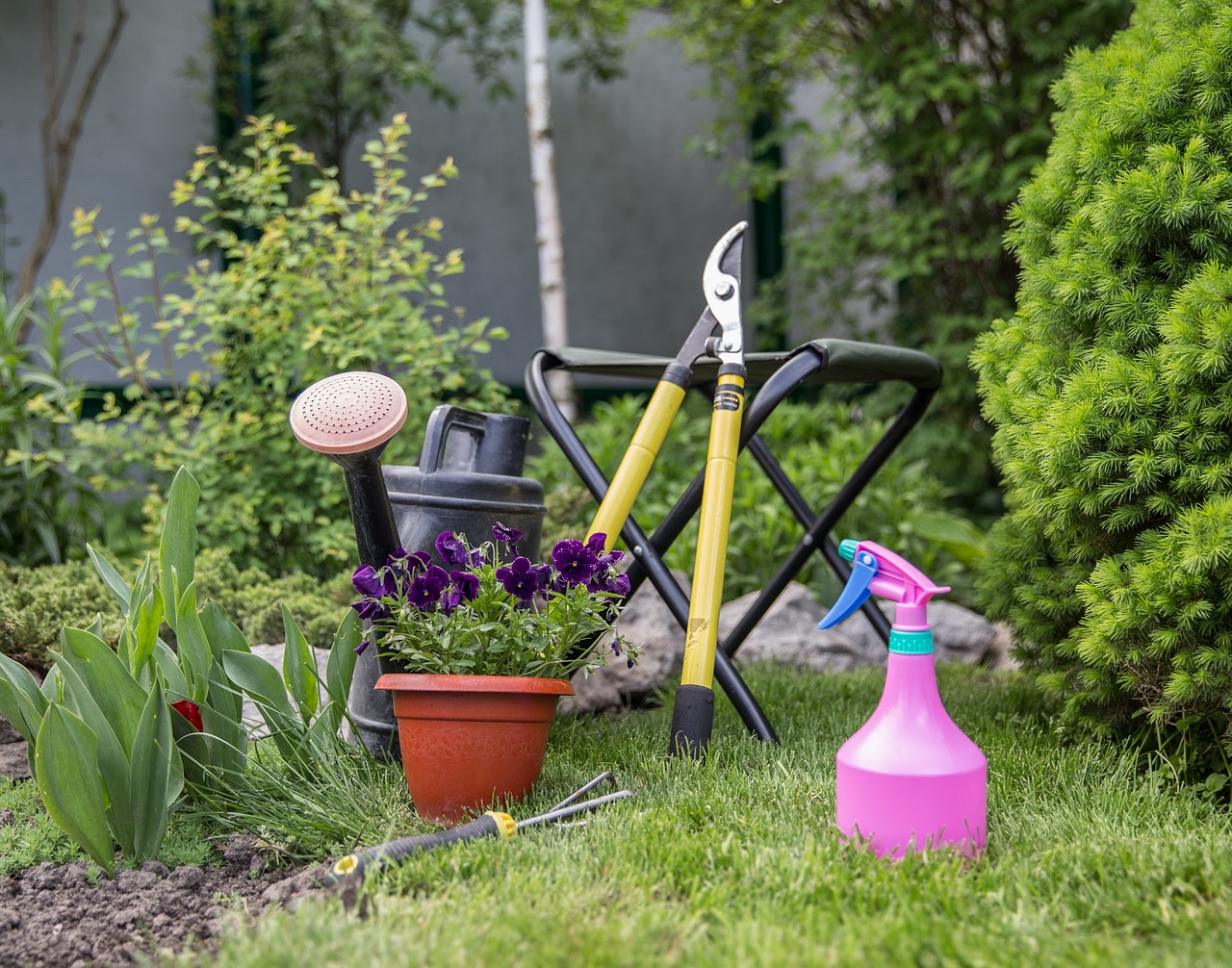
Improved Soil Health
When it comes to gardening, the foundation of success lies beneath the surface—literally! is one of the most significant benefits of incorporating biodiversity into your garden. By introducing a variety of plant species, you are not just beautifying your space; you are also enhancing the very soil that supports your plants. A diverse array of roots and plants creates a complex underground ecosystem that promotes nutrient cycling, increases organic matter, and ultimately leads to a more fertile garden. It's like having a bustling city of microorganisms working tirelessly to keep your soil vibrant and alive!
One of the key ways biodiversity improves soil health is through root interactions. Different plants have varying root structures—some are deep and tap into nutrients far below the surface, while others are shallow and spread out horizontally. This variety allows for a more efficient uptake of nutrients and water. Imagine a team of specialists working together; each plant plays its role, ensuring that no nutrient goes to waste. The result? A robust soil structure that can support a wider range of plant life.
Moreover, the contribution of organic matter from diverse plants cannot be overstated. As plants shed leaves, flowers, and roots, they decompose and enrich the soil with essential nutrients. This organic matter not only provides food for soil organisms but also improves soil structure, enhancing its ability to retain moisture and nutrients. A table summarizing the benefits of organic matter from various plant types can illustrate this point:
| Plant Type | Organic Matter Contribution | Soil Health Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Legumes | Fix nitrogen in the soil | Enhances fertility |
| Grasses | Deep roots add structure | Improves aeration |
| Perennials | Continuous leaf litter | Increases organic matter |
In essence, the more diverse your garden, the healthier your soil will be. By fostering a rich mix of plants, you are creating a thriving ecosystem that supports not only your garden but also the surrounding environment. It's a win-win situation! So, the next time you're planning your garden layout, remember that each plant you choose contributes to a healthier, more resilient soil. The earth beneath your feet is a living, breathing entity, and by embracing biodiversity, you're giving it the love and care it deserves.
- What is biodiversity in gardening? Biodiversity refers to the variety of plant and animal life in a particular habitat, which in gardening means incorporating different species of plants to create a balanced ecosystem.
- How does biodiversity improve soil health? Biodiversity improves soil health through root interactions and the contribution of organic matter, enhancing nutrient cycling and soil structure.
- Can I create a biodiverse garden in a small space? Absolutely! You can create a biodiverse garden in small spaces by selecting a variety of plants that fit your area, such as container gardening or vertical gardens.

Root Interactions
When you think about a garden, you might envision vibrant flowers and lush greenery, but there's a bustling world beneath the surface that's just as vital—roots! The interactions between different root systems can significantly enhance the health of your garden. Imagine a bustling city where diverse communities work together; that's what happens underground! Different plant roots don’t just compete for resources; they also cooperate in ways that promote nutrient uptake and improve soil aeration.
For instance, deep-rooted plants can break up compacted soil, allowing water and air to penetrate more easily. This is like having a team of construction workers digging tunnels to ensure everyone has access to vital resources. Meanwhile, shallow-rooted plants can help hold the soil in place and prevent erosion, creating a stable environment for growth. This synergy not only benefits individual plants but also enhances the overall ecosystem.
Moreover, root interactions can lead to a phenomenon known as mycorrhizal networks. These are underground fungal connections that link the roots of different plants, allowing them to share nutrients and water. Picture a social network where friends share food and resources; this is what happens in the soil! Through these networks, plants can communicate stress signals and even help each other out during tough times, like a friend lending a hand when you’re in need.
In addition, the diversity of root types can improve soil structure. For example, fibrous roots can create a dense mat that holds soil together, while taproots can penetrate deeper layers, accessing nutrients that other plants might miss. This variety is crucial for maintaining soil health and fertility, as it promotes a rich ecosystem of microorganisms that thrive in a well-aerated, nutrient-rich environment.
So, when planning your eco-friendly garden, consider the relationships between plants at the root level. By incorporating a mix of root types, you can create a thriving underground community that supports the entire garden ecosystem. This holistic approach not only enhances plant health but also contributes to the resilience of your garden against pests and diseases. Isn’t it fascinating how much is happening right beneath our feet?
- What are root interactions? Root interactions refer to the ways in which different plant roots influence each other, including competition for resources and cooperation through shared networks.
- How do root interactions benefit my garden? They improve soil health, enhance nutrient uptake, and promote overall plant resilience, leading to a more vibrant and productive garden.
- Can all plants benefit from root interactions? Yes, diverse plant species can create a more complex root system that supports better soil structure and health.
- What are mycorrhizal networks? Mycorrhizal networks are underground fungal connections that link plant roots, allowing for nutrient and water sharing among different plants.

Organic Matter Contribution
When we think about the health of our garden soil, organic matter plays a starring role. It's like the magic ingredient that transforms lifeless dirt into a vibrant ecosystem teeming with life. But what exactly is organic matter? In simple terms, it refers to the decomposed remains of plants and animals, along with other organic materials. This rich substance is vital for enhancing soil structure, fertility, and overall health. By incorporating a variety of plants in your garden, you're not just beautifying your space; you're also contributing to the creation of this essential organic matter.
As plants grow, they naturally shed leaves, stems, and roots. This plant litter breaks down over time, enriching the soil with nutrients. Think of it as nature's way of recycling! When diverse plant species coexist, they produce different types of organic matter, which means a wider range of nutrients becomes available for soil organisms. This diversity is crucial because it promotes a balanced ecosystem in the soil, allowing various microorganisms to thrive. These microorganisms, in turn, help break down organic materials, making nutrients accessible to plants.
Moreover, the roots of different plants interact in fascinating ways. For instance, some plants have deep taproots that can bring up nutrients from deep within the soil, while others have shallow roots that spread out and capture surface nutrients. This root diversity not only enhances nutrient uptake but also improves soil aeration, leading to healthier roots and better water infiltration. Just imagine a bustling city where every resident has a unique job that contributes to the community's well-being; that's what a diverse root system does for your garden's soil!
In addition to these benefits, organic matter significantly improves soil structure. Healthy soil should be crumbly and well-aerated, allowing water and air to penetrate easily. When you have a rich layer of organic matter, it binds soil particles together, creating aggregates that improve drainage and reduce erosion. This is especially important during heavy rains, where well-structured soil can absorb more water, preventing runoff and promoting groundwater recharge.
To visualize the importance of organic matter, consider this table that outlines its key contributions:
| Contribution | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutrient Supply | Provides essential nutrients for plant growth through decomposition. |
| Soil Structure | Improves soil aeration and water retention through aggregation. |
| Microbial Activity | Supports a diverse range of microorganisms that enhance soil health. |
| Erosion Control | Reduces soil erosion by improving the stability of soil aggregates. |
In summary, the contribution of organic matter is a cornerstone of eco-friendly gardening. By fostering a diverse array of plants, you are actively participating in a cycle that not only nourishes the soil but also supports a thriving garden ecosystem. The beauty of this process is that it’s a win-win situation: you get a flourishing garden, and the earth gets healthier soil. Isn't that a fantastic way to cultivate both beauty and sustainability?
- What is organic matter and why is it important? Organic matter consists of decomposed plant and animal material that enriches soil, improves fertility, and supports microbial life.
- How can I increase organic matter in my garden? You can increase organic matter by adding compost, planting cover crops, and incorporating diverse plant species that contribute litter and root decay.
- Does organic matter help with water retention? Yes, organic matter improves soil structure, allowing it to retain moisture more effectively, which is crucial during dry periods.

Pest Control Strategies
Pest control is a significant concern for gardeners, but did you know that embracing biodiversity can be your secret weapon? Instead of relying on chemical pesticides that can harm the environment, a diverse garden ecosystem naturally regulates pests through various mechanisms. Think of your garden as a small community where different species work together to maintain balance. Just like a well-functioning team, each member plays a vital role in keeping the garden healthy and thriving.
One of the primary ways biodiversity aids in pest control is through predation. When you introduce a variety of plants, you also attract a diverse range of beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, which feed on common garden pests like aphids. By creating a habitat that supports these natural predators, you reduce the need for artificial interventions. Additionally, competition among plant species can help deter pests. For instance, when certain plants are grown together, they can create a more complex environment that confuses and repels unwanted insects.
Another effective pest control strategy is to implement companion planting. This technique involves pairing plants that benefit each other, promoting a healthier garden ecosystem. For example, planting marigolds alongside vegetables can deter nematodes and other pests, while herbs like basil can repel flies and mosquitoes. Here’s a quick overview of some effective companion plants:
| Plant | Companion Plant | Pest Deterrent |
|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | Basil | Flies, mosquitoes |
| Cabbage | Mint | Cabbage moths |
| Carrots | Onions | Carrot flies |
Moreover, maintaining a healthy balance of plant diversity can help prevent the spread of pests and diseases. When plants are genetically similar, they are more susceptible to infestations and outbreaks. By diversifying your plant selection, you create a more resilient garden that can withstand pest pressures. This is akin to having a diverse group of friends; if one friend is going through a tough time, the others can help support and uplift them, ensuring that the group remains strong.
Lastly, consider incorporating trap crops into your garden. These are plants that attract pests away from your main crops. By luring pests to these sacrificial plants, you can protect your more valuable plants from damage. For example, planting radishes can attract flea beetles, allowing your other vegetables to flourish without the threat of these pests.
In conclusion, adopting pest control strategies that leverage biodiversity not only promotes a healthier garden but also contributes to a more sustainable approach to gardening. By fostering an environment where natural predators thrive, implementing companion planting, and utilizing trap crops, you can effectively manage pests while minimizing your ecological footprint. So, the next time you think about reaching for that pesticide, consider how a vibrant and diverse garden can be your best ally in the fight against pests.
- What is biodiversity in gardening? Biodiversity in gardening refers to the variety of plant and animal life within a garden ecosystem, which can enhance resilience and sustainability.
- How can I attract beneficial insects to my garden? Planting a diverse range of flowering plants and providing habitats, such as insect hotels, can attract beneficial insects.
- What are trap crops and how do they work? Trap crops are plants that attract pests away from main crops, acting as a decoy to protect more valuable plants.
- Is chemical pesticide use harmful to my garden? Yes, chemical pesticides can harm beneficial insects and disrupt the ecological balance in your garden.

Encouraging Pollinators
When it comes to creating a vibrant and thriving garden ecosystem, one of the most crucial elements to consider is the role of pollinators. These little heroes, including bees, butterflies, and even some birds, are essential for the reproduction of many plants. Without them, our gardens would lack the colorful blooms and delicious fruits we cherish. So, how can we attract and support these vital creatures in our eco-friendly gardening practices? It's all about planting a variety of flowering species that provide food and habitat.
To kick things off, let’s talk about native plants. Native species are not only well-adapted to the local climate and soil conditions, but they also play a significant role in supporting local pollinator populations. When you choose to plant native flora, you’re essentially rolling out the red carpet for your local pollinators. For instance, plants like coneflowers, milkweed, and black-eyed Susans are known to attract a diverse range of pollinators. By incorporating these plants into your garden, you're making a conscious effort to create a sanctuary for these important insects.
But it doesn't stop there! Creating pollinator habitats is equally important. Think of your garden as a mini-ecosystem where different species can thrive. You can achieve this by designing areas that cater to the needs of various pollinators. For example, consider adding:
- Flowering plants: A mix of flowers that bloom at different times throughout the year ensures a consistent food source.
- Water sources: Small water features or shallow dishes filled with pebbles and water can provide hydration.
- Nesting sites: Leaving some areas of bare soil or incorporating bee hotels can help solitary bees find a place to nest.
By incorporating these elements, you not only create a beautiful garden but also a thriving habitat for pollinators. Remember, a garden that attracts pollinators is not just visually appealing; it's also a critical part of maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance. The more diverse habitats you create, the more likely you are to see a variety of pollinators visiting your garden.
Finally, it's essential to consider the use of chemical pesticides. While they might seem like a quick fix for pest problems, they can have detrimental effects on pollinator populations. Instead, embrace natural pest control methods. For instance, introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs can help keep pest populations in check without harming your pollinator friends. By taking these steps, you're not just encouraging pollinators; you're fostering a healthier garden ecosystem.
Q: What are the best plants to attract pollinators?
A: Some of the best plants include native wildflowers like coneflowers, bee balm, and milkweed. These plants provide nectar and pollen that pollinators love!
Q: How can I create a habitat for bees in my garden?
A: You can create a bee-friendly habitat by planting a variety of flowering plants, providing nesting sites like bee hotels, and avoiding chemical pesticides.
Q: Do I need to plant a lot of flowers to attract pollinators?
A: While more flowers can attract more pollinators, even a few well-chosen plants can make a difference. Aim for a mix of plants that bloom at different times to provide year-round food sources.

Native Plants and Pollinators
When it comes to creating a vibrant garden that not only looks stunning but also supports local wildlife, native plants are the unsung heroes. These plants have evolved over thousands of years to thrive in their specific environments, making them perfectly adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. This adaptation means they require less water and fewer resources compared to non-native species, which often struggle to survive outside their natural habitats.
But why are native plants particularly important for pollinators? Well, pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds have developed intricate relationships with local flora. They rely on these plants for food and habitat, making the presence of native species crucial for their survival. For example, many native flowering plants provide the nectar and pollen that these creatures need to thrive. Without native plants, pollinator populations can dwindle, leading to a cascade of ecological problems.
In fact, studies have shown that gardens filled with native plants can attract up to 50% more pollinators than those filled with non-natives. This is because native plants bloom at the right times of the year, providing a consistent food source when pollinators are active. By incorporating a variety of native species into your garden, you create a buffet for these beneficial insects, encouraging them to visit and stay.
But it’s not just about providing food; native plants also offer essential habitats. Many pollinators require specific plants for laying their eggs, and without these plants, populations can decline. For instance, the monarch butterfly relies exclusively on milkweed for its lifecycle. If milkweed is absent from your garden, you won't see these beautiful butterflies fluttering about.
To help you get started, here’s a quick table of some popular native plants and the pollinators they attract:
| Native Plant | Attracted Pollinators |
|---|---|
| Milkweed | Monarch Butterflies |
| Echinacea (Coneflower) | Bees, Butterflies |
| Black-eyed Susan | Bees, Butterflies |
| Bee Balm | Hummingbirds, Bees |
| Goldenrod | Bees, Butterflies |
In conclusion, planting native species is a simple yet powerful way to support pollinator populations. By selecting the right plants, you can create a thriving ecosystem in your garden that not only beautifies your space but also contributes to the health of the environment. So next time you're planning your garden, remember to think local and go native!
Q: Why should I choose native plants over non-native ones?
A: Native plants are better suited to local climates and soils, requiring less maintenance, water, and fertilizer. They also support local wildlife, particularly pollinators.
Q: How can I find out which native plants are suitable for my area?
A: You can consult local gardening centers, native plant societies, or online resources that focus on your region's flora to discover the best native species for your garden.
Q: Do native plants bloom at the same time as non-native plants?
A: Native plants often have specific blooming periods that align with the life cycles of local pollinators, ensuring they provide food when it's most needed.

Creating Pollinator Habitats
This article explores how biodiversity enhances eco-friendly gardening practices, promoting sustainability, resilience, and ecological balance. Discover the benefits, strategies, and various elements that contribute to a thriving garden ecosystem.
Understanding biodiversity is crucial for eco-friendly gardening. It encompasses the variety of life forms that contribute to ecosystem health, resilience, and productivity, ultimately supporting sustainable practices and enhancing the beauty of gardens.
Incorporating diverse plant species in your garden can lead to improved soil health, pest control, and pollination. This section discusses the specific advantages of using a variety of plants in eco-friendly gardening.
Diverse plant species contribute to healthier soil by enhancing nutrient cycling and organic matter. This section examines how a variety of roots and plant types can improve soil structure and fertility.
Different root systems interact in ways that benefit nutrient uptake and soil aeration. This subheading delves into how these interactions promote a healthier underground ecosystem.
Plants contribute organic matter through litter and root decay, enriching the soil. This section explains how diverse plants enhance soil biodiversity and overall health.
Biodiversity can naturally regulate pests through predation and competition. This section highlights how a diverse garden ecosystem can reduce the need for chemical pesticides.
Planting a variety of flowering species attracts different pollinators, which are essential for plant reproduction. This section discusses the importance of pollinator-friendly plants in eco-friendly gardening.
Using native plants can significantly enhance pollinator populations. This subheading explores the relationship between native flora and local pollinator species.
Creating a welcoming habitat for pollinators in your garden is not just beneficial; it’s essential for the environment. Pollinators like bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds play a vital role in the reproduction of many plants. To attract these important creatures, consider the following strategies:
- Plant Diversity: Incorporate a variety of flowering plants that bloom at different times throughout the growing season. This ensures that there is a continuous food source available for pollinators.
- Nectar and Pollen Sources: Choose plants that are rich in nectar and pollen. Native wildflowers, such as coneflowers and black-eyed Susans, are excellent choices.
- Provide Shelter: Create nooks and crannies in your garden where pollinators can rest and hide from predators. Dense shrubs and tall grasses can serve as perfect shelters.
- Water Sources: Pollinators also need water. A shallow dish filled with water and pebbles can provide a safe drinking spot for them.
By designing your garden with these features in mind, you create a thriving ecosystem that supports not only pollinators but also the overall health of your garden. Think of your garden as a small community where every element plays a role in maintaining harmony and balance.
Biodiversity can aid in water conservation through plant selection and arrangement. This section discusses how diverse plantings can improve water retention and reduce irrigation needs.
Incorporating drought-resistant species can significantly lower water usage. This subheading explores the benefits of selecting plants that thrive in low-water conditions.
Different plants contribute to better soil moisture retention. This section explains how a diverse garden can help maintain optimal moisture levels, reducing the need for frequent watering.
Q: How can I start creating a pollinator-friendly garden?
A: Begin by researching native plants that attract local pollinators. Incorporate a variety of these plants into your garden and ensure they bloom at different times of the year.
Q: Do I need to avoid using pesticides altogether?
A: While it's best to minimize pesticide use, if necessary, opt for organic solutions that are less harmful to pollinators.
Q: How much space do I need to create a pollinator habitat?
A: Even a small balcony or patio can support pollinators. Use pots and containers filled with pollinator-friendly plants to create a welcoming space.

Water Conservation Techniques
Water conservation is a fundamental aspect of eco-friendly gardening, and biodiversity plays a pivotal role in achieving this goal. By selecting and arranging a diverse array of plants, gardeners can create a more resilient ecosystem that not only thrives but also efficiently uses water resources. Imagine your garden as a vibrant community where each plant contributes to the overall well-being, much like a group of friends who support each other in times of need. This synergy among plants can lead to improved water retention and reduced irrigation requirements, making your garden not just beautiful but also sustainable.
One of the most effective strategies for water conservation in gardening is the incorporation of drought-resistant plants. These plants, often native to arid regions, have adapted to survive with minimal water. By choosing such species, you can significantly lower your garden's overall water usage. For instance, plants like succulents, lavender, and certain grasses require far less water than traditional garden favorites. Not only do they thrive in dry conditions, but they also add unique textures and colors to your garden, creating an eye-catching landscape.
Additionally, the arrangement of plants can enhance soil moisture management. Different plants have varying root depths and structures, which can significantly impact how water is absorbed and retained in the soil. For example, deep-rooted plants can tap into moisture stored deeper in the ground, while shallow-rooted plants can help cover the soil, reducing evaporation. This interaction creates a balanced ecosystem where moisture levels are maintained more effectively. In fact, studies show that gardens with a mix of plant types can retain up to 30% more moisture compared to monoculture gardens.
| Plant Type | Water Needs | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Drought-Resistant Plants | Low | Requires minimal watering; thrives in dry conditions |
| Native Plants | Moderate | Adapted to local climate; supports local wildlife |
| Ground Covers | Low | Reduces soil evaporation; suppresses weeds |
Moreover, creating a garden with a variety of plant heights and structures not only adds visual interest but also aids in moisture retention. Taller plants can provide shade to smaller ones, reducing the amount of direct sunlight that hits the soil and consequently lowering evaporation rates. This layered approach mimics natural ecosystems, where plants work together to create a microclimate that retains moisture.
As you plan your garden, consider incorporating mulch around your plants. Mulching is another effective technique that helps conserve water by minimizing soil evaporation. Organic mulches, such as wood chips or straw, not only retain moisture but also decompose over time, enriching the soil with organic matter. This creates a win-win situation where your garden remains hydrated while also improving soil health.
In summary, embracing biodiversity in your gardening practices is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for sustainable living. By selecting drought-resistant plants, arranging them thoughtfully, and employing mulching techniques, you can significantly enhance your garden’s water conservation capabilities. Remember, every small step you take in your garden contributes to a larger movement towards ecological balance and sustainability.
- What are the best drought-resistant plants for my garden?
Some popular options include succulents, lavender, and ornamental grasses. These plants require minimal water and thrive in dry conditions.
- How can I improve soil moisture retention?
Incorporate organic mulch, select a variety of plant types with different root depths, and ensure proper spacing to reduce evaporation.
- Is it necessary to water my garden every day?
No, with a diverse planting strategy and proper soil management, your garden can thrive with less frequent watering.

Drought-Resistant Plants
When it comes to gardening in arid conditions, are nothing short of heroes. These resilient plants are specially adapted to thrive in low-water environments, making them ideal choices for eco-friendly gardens. Imagine a garden that not only looks beautiful but also conserves water—sounds like a dream, right? Well, it’s entirely achievable with the right plant selections!
Drought-resistant plants have evolved unique features that allow them to withstand prolonged periods of dryness. For instance, many of these plants possess deep root systems that can tap into underground water sources, while others have thick, waxy leaves that minimize water loss through evaporation. This natural adaptation not only helps them survive but also contributes to a more sustainable gardening practice.
Let’s take a closer look at some popular drought-resistant plants that can transform your garden into a vibrant oasis while conserving precious water:
- Lavender: Known for its aromatic scent and beautiful purple flowers, lavender thrives in hot, dry conditions and attracts pollinators.
- Agave: This succulent is a striking addition to any garden, with its architectural leaves and minimal water requirements.
- Succulents: These water-storing plants come in various shapes and sizes, making them perfect for adding texture and color while needing very little water.
- Russian Sage: With its silvery foliage and tall spikes of lavender-blue flowers, this plant not only looks stunning but is also incredibly drought-tolerant.
Incorporating these plants into your garden design can significantly lower your water usage. However, it’s not just about picking the right plants; it’s also about how you arrange them. Grouping drought-resistant plants together can create microclimates that enhance their ability to thrive. For example, taller plants can provide shade for shorter ones, reducing their water needs even further. It’s like creating a community where each plant supports the other—how cool is that?
Another key aspect of maintaining a drought-resistant garden is soil management. Amending your soil with organic matter can improve its structure, allowing it to retain moisture more effectively. A well-aerated soil not only helps your plants access nutrients but also encourages deep root growth, which is essential for drought resilience. Think of it as giving your plants a solid foundation to build their homes on, ensuring they can weather the toughest of droughts.
Ultimately, choosing drought-resistant plants is not just a smart choice for the environment; it’s also an opportunity to showcase your creativity as a gardener. With a little planning and a keen eye for aesthetics, you can create a stunning landscape that thrives even in the driest conditions.
1. What are drought-resistant plants?
Drought-resistant plants are species that have adapted to survive with minimal water. They often have deep roots, thick leaves, or special water-storing capabilities.
2. Why should I use drought-resistant plants in my garden?
Using drought-resistant plants can significantly reduce your water consumption, promote sustainability, and create a low-maintenance garden that thrives in dry conditions.
3. Can drought-resistant plants still require watering?
Yes, while drought-resistant plants are more resilient, they still need some water, especially during their establishment phase. Once established, they can thrive with minimal irrigation.
4. Are drought-resistant plants suitable for all climates?
While they are ideal for arid and semi-arid climates, many drought-resistant plants can also thrive in other environments with proper care and soil management.

Soil Moisture Management
Soil moisture management is a critical aspect of eco-friendly gardening that can make or break the success of your plants. Imagine your garden as a thirsty traveler in a desert; without adequate moisture, it simply cannot thrive. By incorporating a variety of plant species, you can create a dynamic ecosystem that enhances moisture retention in the soil. Different plants have unique root structures and moisture needs, which can work together to maintain optimal humidity levels in the soil. For example, deep-rooted plants can tap into moisture reserves that are unavailable to shallow-rooted species, effectively utilizing every drop of water available.
Moreover, the arrangement of plants plays a significant role in moisture management. When you plant in layers—tall plants providing shade for shorter ones—you create a microclimate that reduces evaporation. This is akin to how a forest canopy protects the undergrowth from the harsh sun. Additionally, ground cover plants can act as a living mulch, preventing soil erosion and reducing water loss through evaporation. This symbiotic relationship among plants not only conserves water but also promotes a healthier garden ecosystem.
To further enhance soil moisture retention, consider the following strategies:
- Mulching: Applying organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, can significantly reduce moisture loss. It acts as a barrier against the sun and helps maintain consistent soil temperatures.
- Soil Amendments: Incorporating organic matter like compost can improve soil structure, allowing it to hold onto moisture more effectively. Healthy soil is like a sponge, soaking up water and releasing it slowly to plants.
- Watering Techniques: Utilizing drip irrigation systems can deliver water directly to the roots, minimizing evaporation and ensuring that plants receive the moisture they need without waste.
In conclusion, managing soil moisture through biodiversity is not just an effective gardening technique; it's a sustainable practice that helps conserve resources. By creating a diverse garden, you foster an environment where plants can thrive together, each contributing to the overall health of the ecosystem. So, as you cultivate your garden, think of it as a community, where every plant plays its part in the grand design of nature.
Q1: How does biodiversity affect soil moisture?
A1: Biodiversity enhances soil moisture retention by promoting various root systems that work together to utilize water efficiently and reduce evaporation.
Q2: What are some drought-resistant plants I can incorporate?
A2: Some popular drought-resistant plants include lavender, succulents, and native grasses, which thrive in low-water conditions.
Q3: How often should I water my garden to maintain soil moisture?
A3: It depends on the plants you have, but generally, watering deeply once a week is more effective than shallow watering more frequently.
Q4: Can mulch really make a difference in moisture retention?
A4: Absolutely! Mulch acts as a protective layer, reducing evaporation and keeping the soil temperature stable, which is vital for moisture retention.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is biodiversity, and why is it important in eco-friendly gardening?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms in a given ecosystem, including different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms. In eco-friendly gardening, biodiversity is crucial because it enhances ecosystem health, resilience, and productivity. A diverse garden can better withstand pests and diseases, improve soil quality, and promote a balanced ecosystem.
- How can diverse plant species improve soil health?
Diverse plant species contribute to healthier soil by enhancing nutrient cycling and organic matter. Different root systems interact in ways that boost nutrient uptake and soil aeration. Moreover, as plants decay, they add organic matter to the soil, enriching it and fostering a thriving underground ecosystem.
- Can biodiversity help with pest control?
Absolutely! A diverse garden ecosystem can naturally regulate pests through predation and competition. By incorporating a variety of plants, you can attract beneficial insects that prey on pests, thus reducing the need for chemical pesticides and promoting a healthier garden environment.
- What role do pollinators play in eco-friendly gardening?
Pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, are essential for plant reproduction. By planting a variety of flowering species, you can attract different pollinators to your garden. This not only enhances the beauty of your garden but also ensures that your plants can produce seeds and fruits effectively.
- How can I create a habitat for pollinators in my garden?
Creating a habitat for pollinators involves designing your garden with diverse plants and environments. Incorporate native plants that local pollinators prefer, provide water sources, and create sheltered areas for resting. The more inviting your garden is, the more pollinators will thrive!
- What are some effective water conservation techniques for gardeners?
To conserve water, consider using drought-resistant plants, which require less irrigation. Additionally, arranging plants to improve water retention and using mulch can significantly reduce evaporation. A diverse garden can help maintain optimal moisture levels, making your watering routine more efficient.
- How do drought-resistant plants benefit eco-friendly gardening?
Drought-resistant plants are fantastic for saving water and promoting sustainability. They thrive in low-water conditions, which means you won’t have to water them as frequently. This not only conserves water but also reduces the time and effort spent on garden maintenance.



















