Can Local Food Production Reduce Environmental Impact?
In recent years, the conversation around food production has taken a significant turn towards sustainability. As we become increasingly aware of the environmental challenges facing our planet, many are asking, can local food production really make a difference? The answer is a resounding yes! By focusing on local food systems, we can not only reduce our carbon footprint but also foster healthier communities and economies.
Local food production minimizes transportation distances, which is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. When food is grown closer to where it is consumed, it travels shorter distances, leading to lower fuel consumption and reduced air pollution. Imagine the difference between a tomato that travels thousands of miles from a large industrial farm versus one that is harvested from a nearby garden. This simple shift can significantly decrease the environmental impact associated with food logistics.
Moreover, local food systems promote biodiversity and ecological balance. By supporting local farmers who often use sustainable practices, we can help maintain the health of our ecosystems. These farmers are more likely to engage in crop rotation and organic farming methods, which not only produce healthier food but also protect the soil and water resources. It’s like planting a seed of change that flourishes into a thriving ecosystem.
Additionally, local food production enhances community resilience. When communities prioritize local sources for their food, they create a robust network that is less vulnerable to global market fluctuations. This means that during times of crisis—like natural disasters or economic downturns—local food systems can provide a safety net, ensuring that people have access to fresh and nutritious food. It’s a bit like having a lifebuoy ready when the waves get rough.
In summary, the benefits of local food production extend far beyond just reducing environmental impact. It fosters a sense of community, supports local economies, and encourages sustainable practices that can lead to a healthier planet. So, the next time you’re at the grocery store or a farmers' market, consider the profound impact your choices can have—not just on your plate, but on the world around you.
- How does local food production reduce carbon emissions? Local food production reduces carbon emissions by minimizing transportation distances, which lowers fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- What are the economic benefits of supporting local farmers? Supporting local farmers can create jobs, enhance economic resilience, and keep money circulating within the community.
- Are local foods healthier than mass-produced alternatives? Yes, local foods are often fresher and more nutrient-dense, leading to better health outcomes for consumers.
- What challenges do local food producers face? Local food producers face challenges such as seasonality, competition with industrial agriculture, and scalability issues.
- How can communities promote local food systems? Communities can promote local food systems through policy advocacy, community engagement initiatives, and consumer education.
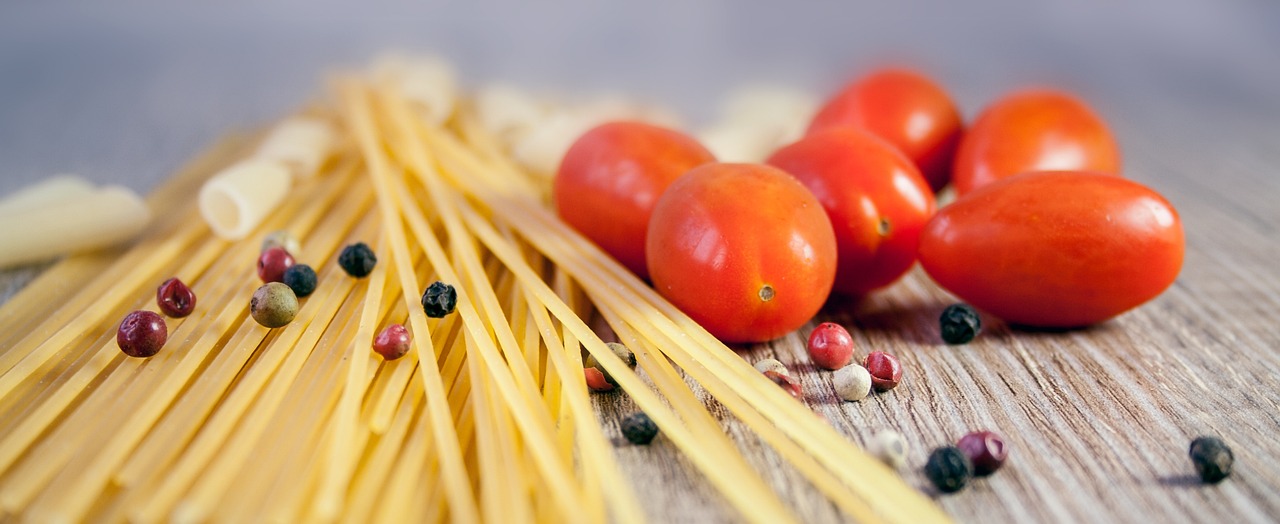

The Environmental Benefits of Local Food
When we think about our food, we often overlook the journey it takes to reach our plates. Local food production is a game-changer in this regard, significantly reducing our carbon footprints by minimizing transportation distances. Imagine a world where your fruits and vegetables travel mere miles instead of thousands; this shift can lead to a remarkable decrease in greenhouse gas emissions. It’s like swapping a long, winding road trip for a quick stroll down the street!
Not only does sourcing food locally cut down on emissions, but it also promotes ecological balance. Local farms tend to use more sustainable practices, as they are deeply intertwined with their communities. This connection fosters a sense of responsibility toward the land and its resources. For instance, local farmers are more likely to engage in crop rotation, organic farming, and sustainable pest management, which can lead to healthier ecosystems. By choosing local, you're not just feeding yourself; you're nurturing the environment.
Furthermore, local food systems encourage biodiversity. When you buy from local farmers, you often have access to a wider variety of produce, including heirloom varieties that you wouldn’t find in a supermarket. This diversity is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems. It’s like having a colorful palette of paint; the more colors you have, the more vibrant your picture becomes. In this case, a diverse agricultural landscape leads to a more resilient environment.
Another significant benefit of local food production is its impact on water conservation. Local farms, particularly those that practice sustainable methods, often utilize techniques that reduce water usage and prevent runoff. This is essential in combating issues like soil erosion and water pollution. To illustrate, here’s a simple comparison:
| Aspect | Local Food Production | Industrial Agriculture |
|---|---|---|
| Transportation Emissions | Low | High |
| Water Usage | Conservative | High |
| Biodiversity | High | Low |
As you can see, local food production not only benefits the environment but also creates a ripple effect that enhances community well-being. When people are more aware of where their food comes from, they tend to make more informed choices, fostering a culture of sustainability. It’s like planting a seed; with care and attention, it grows into something beautiful and beneficial for all.
In conclusion, the environmental benefits of local food production are multifaceted and profound. By choosing to support local farmers, we are not only making a healthier choice for ourselves but also taking a stand for the planet. Isn’t it time we embraced this change and made a commitment to our local food systems?
- What are the main environmental benefits of local food? Local food reduces transportation emissions, promotes biodiversity, conserves water, and encourages sustainable farming practices.
- How does local food support the community? It boosts the local economy, creates jobs, and fosters a sense of community pride and responsibility.
- Can local food systems compete with industrial agriculture? Yes, with the right policies and consumer support, local food systems can thrive despite competition from industrial agriculture.
Economic Advantages of Supporting Local Farmers
When we think about the impact of our food choices, it's easy to overlook the economic advantages that come with supporting local farmers. Investing in local food systems is not just a trendy choice; it’s a powerful way to revitalize our communities and boost local economies. When you buy from local farmers, you’re not just purchasing fresh produce; you’re also injecting money directly into your community. This creates a ripple effect that can lead to job creation, increased economic resilience, and a stronger sense of community.
One of the most immediate benefits of supporting local farmers is the creation of jobs. Local agriculture requires a variety of roles, from farming to processing and distribution. These jobs are often more stable than those in larger, industrial settings because they are deeply rooted in the community. When people are employed locally, they are more likely to spend their earnings within the community, further enhancing economic growth. According to recent studies, every dollar spent on local food can generate up to four times its value in local economic activity.
Moreover, local food systems can help communities become more economically resilient. In times of global market fluctuations, local farmers can provide a stable source of food and income. By prioritizing local over imported goods, communities can shield themselves from the volatility of global supply chains. This resilience is particularly important in times of crisis, such as during natural disasters or pandemics, when access to food can become a challenge. When local farmers thrive, the entire community benefits, leading to a more sustainable and secure food system.
Additionally, supporting local farmers fosters an environment of skill development and innovation. When communities rally behind their local agriculture, they often create programs that offer training and workshops. These initiatives empower individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to engage in farming and food production. For instance, many local organizations host events where community members can learn about sustainable farming practices, cooking classes, and even nutrition workshops. This not only enhances individual skill sets but also encourages a culture of self-sufficiency.
Another crucial aspect of local food systems is their ability to boost local markets. Farmers' markets and community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs thrive when communities actively support local farmers. These markets not only provide access to fresh, nutritious food but also serve as vibrant community spaces where people can connect. They foster a sense of belonging and encourage social interactions, which are vital for community cohesion. By supporting these markets, you’re not just buying food; you’re investing in the social fabric of your community.
In conclusion, the economic advantages of supporting local farmers are profound and far-reaching. From job creation to economic resilience and community engagement, local food systems offer a multitude of benefits that can transform communities. By choosing to buy local, we can all play a part in building a more sustainable and prosperous future for our communities.
- Why should I buy local food? Purchasing local food supports your community's economy, reduces carbon footprints, and often provides fresher produce.
- How does buying local create jobs? Local food systems require labor for farming, processing, and distribution, which creates job opportunities within the community.
- Are local foods more expensive? While some local foods may be pricier, they often reflect the true cost of sustainable farming and can lead to savings in health and environmental costs.
- How can I find local farmers? You can discover local farmers through farmers' markets, community-supported agriculture programs, and local food directories.

Job Creation in Local Agriculture
Local agriculture isn't just about growing food; it's a powerhouse for job creation within communities. When we support local farmers, we’re not just filling our plates with fresh produce; we’re also filling job openings that help sustain our neighborhoods. Think about it: every time you buy from a local farmer's market, you're contributing to a cycle of employment that touches various sectors, from farming to processing and distribution.
In fact, local food systems can create a diverse array of jobs, including:
- Farmers: The backbone of local agriculture, farmers cultivate crops and raise livestock, directly contributing to food production.
- Food Processors: These individuals prepare and package local foods, ensuring they reach consumers in top condition.
- Logistics and Distribution Workers: They handle the transportation of local goods, making sure everything from fresh vegetables to artisanal cheeses gets to market efficiently.
- Retail Staff: Local markets and co-ops require employees to manage sales, customer service, and inventory.
But it doesn’t stop there. Local agriculture also fosters opportunities for entrepreneurship. With the growing demand for organic and locally sourced products, many individuals are stepping up to start their own businesses, whether it's a small farm, a food truck, or a community-supported agriculture (CSA) program. This entrepreneurial spirit not only creates jobs but also enhances the local economy by keeping money circulating within the community.
Moreover, local food initiatives often lead to the development of training programs that equip individuals with essential agricultural skills. These programs can range from workshops on sustainable farming practices to hands-on training in food processing techniques. By investing in education, communities are not only preparing the next generation of farmers but also creating a skilled workforce ready to tackle the challenges of modern agriculture.
Ultimately, the job creation potential of local agriculture extends beyond just employment numbers. It builds a sense of community, fosters economic resilience, and strengthens the bonds between consumers and producers. When we buy local, we’re not just supporting farmers; we’re investing in our own communities and ensuring a sustainable future for everyone.
- What are the main benefits of local food production? Local food production reduces transportation emissions, supports local economies, and provides fresher, healthier food options.
- How can I support local farmers? You can support local farmers by shopping at farmers' markets, joining a CSA, or purchasing from local grocery stores that prioritize local products.
- Are local foods more expensive? While some local foods may be pricier, they often reflect the true cost of sustainable farming practices and can be more nutritious.
- What challenges do local farmers face? Local farmers may struggle with competition from industrial agriculture, seasonal availability of crops, and limited access to markets.

Skill Development Opportunities
When it comes to local food production, one of the most exciting aspects is the potential for skill development. Communities that prioritize local agriculture often find themselves at the forefront of an educational revolution. By fostering a culture of learning and sharing, these communities can empower individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to thrive in the agricultural sector. Imagine a neighborhood where everyone knows how to grow their own vegetables, or where local workshops teach the art of canning and preserving foods—this is not just a dream, but a reality that can be cultivated.
Local farms and agricultural organizations frequently offer training programs and workshops that cater to various skill levels. These initiatives can cover a wide range of topics, such as:
- Organic farming techniques
- Soil health management
- Crop rotation and companion planting
- Pest management without chemicals
- Food preservation methods
These skill-building opportunities not only enhance individual capabilities but also contribute to the overall resilience of the community. For instance, when individuals gain expertise in sustainable farming practices, they can share their knowledge with others, creating a ripple effect that strengthens the local food system. Additionally, hands-on experience allows participants to develop a deeper appreciation for the food they consume and the labor that goes into producing it.
Moreover, local schools can play a pivotal role by integrating agricultural education into their curricula. Programs that involve students in gardening or farming projects can instill a sense of responsibility and connection to the land from a young age. This not only equips future generations with valuable skills but also fosters a culture of sustainability that can last for decades.
In essence, the opportunities for skill development within local food systems are vast and varied. By investing in education and training, communities can cultivate a knowledgeable workforce that is well-equipped to tackle the challenges of modern agriculture. This not only leads to enhanced food production but also strengthens community ties, creating a more engaged and informed populace.
Q1: How can I get involved in local food production?
A1: You can start by visiting local farmers' markets, joining community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, or participating in workshops offered by local farms.
Q2: What are the benefits of consuming locally produced food?
A2: Local food is often fresher, more nutritious, and supports the local economy. It also reduces the carbon footprint associated with transporting food over long distances.
Q3: Are there any challenges to local food production?
A3: Yes, challenges include seasonality, competition from industrial agriculture, and scalability. However, community engagement and policy advocacy can help overcome these hurdles.
Q4: How can I advocate for local food systems in my community?
A4: You can advocate by supporting local farmers, participating in community meetings, and encouraging local governments to implement policies that benefit local agriculture.

Boosting Local Markets
Local food systems play a crucial role in invigorating local markets, creating a vibrant community atmosphere that fosters both economic growth and social connections. When consumers choose to buy from local farmers, they are not just purchasing fresh produce; they are investing in their community. This creates a multiplier effect where every dollar spent locally circulates within the community, supporting local jobs and businesses. Imagine walking through a bustling farmers' market filled with the colors and aromas of fresh fruits and vegetables, where the very farmers who grew the food are present, ready to share their stories and knowledge. This connection between producers and consumers is invaluable.
Moreover, local markets often prioritize seasonal produce, which not only enhances the flavor and nutritional value of the food but also encourages sustainable farming practices. By purchasing food that is in season, consumers help reduce the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation. For instance, when you buy a basket of strawberries in the summer from a nearby farm, you're supporting local agriculture and enjoying fruit that is at its peak ripeness.
Local markets also provide a platform for small-scale farmers to showcase their products. Unlike large industrial farms, local farmers often grow a diverse array of crops, which can lead to unique offerings that aren't available in conventional grocery stores. This diversity not only enriches the market but also encourages consumers to explore new foods. Consider a local market where you can find heirloom tomatoes, artisanal cheeses, and organic honey, all produced within a few miles of your home. This variety not only excites the palate but also fosters a sense of community identity.
Furthermore, local markets can enhance food accessibility. By establishing community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs or food co-ops, communities can ensure that fresh, healthy food is available to everyone, regardless of income level. These initiatives can be particularly impactful in food deserts, where access to fresh produce is limited. By working together, communities can create solutions that bring nutritious food to all residents, promoting overall well-being.
In summary, boosting local markets is essential for creating a sustainable food system that benefits everyone. The interplay between local farmers and the community not only strengthens the local economy but also fosters a sense of belonging and shared responsibility. As consumers, we have the power to make choices that support our local food systems, leading to healthier communities and a more sustainable planet.
- What are some benefits of buying local food?
Buying local food supports the local economy, reduces carbon footprints, and provides fresher produce. - How can I find local farmers' markets?
You can search online for local farmers' markets or check community boards for listings in your area. - Are local food systems more expensive than conventional grocery stores?
While some local foods may cost more, many consumers find that the quality and freshness justify the price. - How does local food production impact the environment?
Local food production reduces greenhouse gas emissions associated with transportation and promotes sustainable farming practices.

Economic Resilience through Local Food Systems
In today's rapidly changing economic landscape, local food systems emerge as a beacon of hope for communities seeking stability and resilience. By prioritizing local food production, communities can create a safety net against the unpredictable tides of global markets. Imagine a scenario where a community relies less on imports and more on its local farms; this not only enhances food security but also fortifies the local economy.
When communities invest in local agriculture, they are essentially investing in their own economic future. Local food systems can help cushion the blow from economic downturns, as they are less susceptible to the fluctuations of global supply chains. For instance, during times of crisis, such as a pandemic or natural disaster, local food sources can provide essential goods without the delays often associated with long-distance transportation.
Furthermore, supporting local farmers means that money circulates within the community. When consumers buy produce from local markets, they are not just purchasing food; they are supporting local jobs and services. This creates a multiplier effect that strengthens the community's economic fabric. According to recent studies, every dollar spent on local food can generate up to three times that amount in economic activity within the community.
To illustrate this point, consider the following table that outlines the potential economic impacts of investing in local food systems:
| Investment Type | Local Economic Impact |
|---|---|
| Buying Local Produce | Generates $3 for every $1 spent |
| Supporting Local Farmers' Markets | Increases foot traffic and sales for local businesses |
| Investing in Local Food Initiatives | Creates jobs and boosts local employment rates |
Moreover, local food systems can also enhance a community's self-reliance. By developing a robust agricultural sector, communities can become less dependent on external food sources, which is crucial during times of crisis. This self-sufficiency fosters a sense of pride and connection among residents, reinforcing community bonds.
Ultimately, the resilience offered by local food systems is not just about economics; it’s about creating a sustainable future. By emphasizing local production, communities can adapt to changes, support their local farmers, and ensure that they have access to fresh, healthy food. This holistic approach to food production can pave the way for a more secure and prosperous future.
- What are local food systems? Local food systems refer to the networks that connect local producers with consumers, emphasizing the importance of sourcing food from nearby farms.
- How do local food systems promote economic resilience? They reduce dependency on global supply chains, keeping money within the community and creating local jobs.
- Can local food production support job creation? Yes, local food production fosters job opportunities in farming, processing, and distribution sectors.
- What are some challenges faced by local food systems? Challenges include seasonality, competition with industrial agriculture, and scalability.

Health Benefits of Consuming Local Foods
When it comes to health, the phrase "you are what you eat" couldn't ring truer. Consuming locally produced foods can lead to a plethora of health benefits that not only enhance individual well-being but also contribute to community health. One of the most compelling reasons to embrace local foods is their nutritional superiority. Local produce is often harvested at its peak ripeness, which means it retains more nutrients compared to items that have traveled long distances. Imagine biting into a juicy tomato that was picked just hours before; the taste and nutritional value are simply unparalleled!
Moreover, the freshness of local foods can significantly impact your overall health. Fresh fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are essential for maintaining a strong immune system. Studies have shown that the longer food sits after being harvested, the more nutrients it loses. This is especially true for items like leafy greens and berries, which can lose their nutritional potency within days of being harvested. By choosing local, you're not just supporting your local economy but also ensuring that what you consume is at its best.
Another noteworthy aspect of local foods is their potential to enhance food security within communities. When local food systems thrive, they create a reliable source of fresh produce that is less susceptible to global market fluctuations. This means that communities can enjoy consistent access to healthy food options, reducing the risk of food deserts—areas where access to affordable and nutritious food is limited. In essence, local food production can act as a safety net, ensuring that everyone has access to the nourishment they need.
Additionally, the health benefits of consuming local foods extend beyond just the physical. Engaging with local farmers and markets fosters a sense of community well-being. When individuals come together to support local agriculture, they build relationships and create a network of support that enhances social cohesion. This sense of community can lead to improved mental health, as people feel more connected and engaged with their surroundings. It's like a warm hug for your soul!
To illustrate the nutritional differences between local and mass-produced foods, consider the following table:
| Food Item | Nutritional Value (per 100g) | Freshness |
|---|---|---|
| Local Tomato | 18 calories, 0.2g fat, 1.2g protein, 3.9g carbs | Harvested within hours |
| Mass-Produced Tomato | 20 calories, 0.3g fat, 0.9g protein, 4.1g carbs | Transported over several days |
In conclusion, the health benefits of consuming local foods are multifaceted. From enhanced nutritional value to improved community well-being, the advantages are clear. By choosing local, you're not just making a choice for your health; you're also contributing to a healthier community and environment. So, next time you're at the grocery store or farmers' market, remember that every bite of local food is a step towards a healthier you!
- What are the main health benefits of eating local foods? Eating local foods often results in higher nutritional value, better taste, and improved food security.
- How can I find local food sources in my area? You can explore farmers' markets, community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, and local co-ops to find fresh local produce.
- Are local foods always organic? Not necessarily. While many local farms practice organic farming, it's essential to ask about their farming practices.
- How do local foods contribute to community health? Local foods enhance food security, promote social connections, and support local economies, all of which contribute to overall community health.

Nutrition and Freshness
When it comes to food, the nutritional value and freshness of what we consume can drastically affect our health. Local foods often triumph over mass-produced alternatives in both categories. Why is that, you ask? Well, it's all about the journey from farm to table. When food is grown nearby, it spends less time in transit. This means it can be harvested at its peak ripeness, allowing for maximum flavor and nutrient retention. In contrast, foods that travel long distances are typically picked before they reach their prime. This not only diminishes their taste but also their nutritional content.
Consider this: a tomato picked at the height of summer and delivered to your plate the same day is bursting with flavor and vitamins. On the other hand, a tomato that has traveled thousands of miles may have been harvested weeks earlier, losing some of its vital nutrients along the way. Research has shown that local produce can contain significantly higher levels of essential vitamins and minerals. For instance, studies indicate that locally grown vegetables can have:
| Type of Produce | Vitamin C Content (mg per 100g) | Days from Harvest to Table |
|---|---|---|
| Local Tomato | 20 | 1 |
| Imported Tomato | 10 | 14 |
| Local Spinach | 28 | 2 |
| Imported Spinach | 15 | 10 |
This table illustrates just how much of a difference local sourcing can make. The shorter the distance, the fresher the food, and the more nutrients it retains. Additionally, local farmers often use organic practices, which means fewer pesticides and chemicals on your plate. This not only enhances the flavor but also contributes to a healthier diet.
Moreover, when you eat locally, you’re likely consuming foods that are in season. Seasonal foods are naturally more flavorful and nutritious because they are grown in their ideal conditions. For example, root vegetables in the winter are harvested when they are at their sweetest, while summer berries are bursting with juice and flavor. Eating with the seasons not only supports your health but also encourages a diverse diet rich in various nutrients.
In conclusion, the benefits of consuming local foods go beyond just taste. They offer a pathway to better nutrition and a more sustainable lifestyle. By choosing to support local farmers, you are not only investing in your health but also in the well-being of your community and the environment.
- Why should I choose local foods over imported foods? Local foods are fresher, tastier, and often more nutritious than their imported counterparts.
- How can I find local food sources? Look for farmers' markets, local co-ops, or community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs in your area.
- Are local foods more expensive? While some local foods may have a higher price tag, buying directly from farmers can often save you money in the long run.
- What are the environmental benefits of eating locally? Eating locally reduces transportation emissions and supports sustainable farming practices.

Community Well-being and Food Security
When we talk about community well-being, it's impossible to overlook the crucial role that food security plays in this equation. Imagine a community where every individual has reliable access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food. This isn’t just a dream; it’s a reality that can be fostered through local food systems. By prioritizing local food production, communities can ensure that fresh, healthy options are available to everyone, regardless of their economic status.
Local food systems enhance food security by reducing reliance on distant suppliers and industrial agriculture, which can be unstable and unpredictable. When communities grow their own food, they create a buffer against global supply chain disruptions, such as those caused by natural disasters or economic downturns. This self-sufficiency not only strengthens the local economy but also promotes a sense of community pride and ownership.
Moreover, access to fresh, locally sourced produce contributes significantly to the overall health of a community. Studies have shown that individuals who consume locally grown foods tend to have better health outcomes. This is largely due to the nutritional value of fresh produce, which is often harvested at its peak ripeness and brought to market quickly. In contrast, foods that travel long distances often lose vital nutrients along the way. By consuming local foods, community members can enjoy:
- Higher nutrient retention
- Increased variety of fresh produce
- Reduced exposure to harmful preservatives and chemicals
Furthermore, local food systems foster social connections and community engagement. Farmers' markets, community gardens, and local food co-ops serve as gathering places where individuals can connect, share knowledge, and support one another. These interactions build trust and solidarity, leading to a more resilient community. It's not just about food; it's about creating a vibrant social fabric that can withstand challenges.
In conclusion, promoting local food production is a powerful strategy for enhancing both community well-being and food security. By investing in local agriculture, we can create healthier, more connected communities that are better equipped to face the future. As we cultivate our local food systems, we also cultivate a sense of belonging and shared responsibility for our collective health.
- What is food security? Food security means having reliable access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to maintain a healthy life.
- How does local food production improve food security? It reduces dependency on external sources, ensuring that communities can access fresh food even during global disruptions.
- What are some ways to support local food systems? You can support local food systems by shopping at farmers' markets, participating in community-supported agriculture (CSA), and advocating for local food policies.
- Can local food production really boost community health? Yes! Local foods are often fresher and more nutrient-dense, leading to better health outcomes for community members.

Challenges of Local Food Production
While the benefits of local food production are numerous, there are also significant challenges that must be addressed to ensure its success. One of the primary obstacles is seasonality. Local food production is often limited by the growing seasons of various crops. For instance, while you might crave fresh tomatoes in winter, local farmers may not have them available, leading to a reliance on imported goods. This seasonal availability can create gaps in the local food supply, making it difficult for consumers to consistently access fresh produce.
Moreover, the competition with industrial agriculture poses another hurdle. Large-scale farming operations benefit from economies of scale, enabling them to produce food at lower prices than local farmers. This price disparity can make it challenging for local producers to compete, as consumers often gravitate towards cheaper options without considering the environmental and social costs associated with industrial farming. To illustrate this point, consider the following table:
| Factor | Local Food Production | Industrial Agriculture |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Environmental Impact | Lower | Higher |
| Community Support | Stronger | Weaker |
In addition to these factors, there are also logistical challenges that local food systems face. Small-scale farmers often lack the infrastructure and resources necessary to efficiently distribute their products. This can lead to increased food waste and spoilage, particularly when farmers are unable to get their goods to market in a timely manner. Furthermore, without adequate storage facilities, local producers may struggle to maintain their products' freshness, further impacting consumer trust and demand.
Lastly, there is the issue of consumer awareness. Many individuals are simply unaware of the benefits of supporting local food systems. They might not understand how local food production can contribute to a healthier community and a more sustainable environment. Without proper education and outreach, the local food movement may struggle to gain traction, which is why community engagement initiatives are crucial. By fostering a culture of awareness and appreciation for local foods, communities can help bridge the gap between consumers and local producers.
- What are the main challenges of local food production?
The main challenges include seasonality, competition with industrial agriculture, logistical issues, and consumer awareness.
- How can communities support local farmers?
Communities can support local farmers by participating in farmers' markets, advocating for local food policies, and educating others about the benefits of local food systems.
- Are local foods more expensive than imported foods?
Generally, local foods can be more expensive due to smaller scale production and lack of economies of scale, but the environmental and community benefits often outweigh the costs.

Seasonal Availability of Local Produce
When we talk about local food production, one of the most fascinating yet challenging aspects to consider is the seasonal availability of produce. Unlike mass-produced foods that can be shipped in from anywhere at any time, local foods are often bound by the natural rhythms of the seasons. This means that what’s fresh and available can change dramatically throughout the year. Imagine biting into a crisp, juicy apple in the fall or savoring the sweet taste of ripe strawberries in the summer; these experiences are not just delightful, they are also a reflection of the seasonality of local produce.
However, this seasonality can also pose challenges for consumers who are used to having access to a wide variety of foods year-round. For instance, if you live in a region that grows tomatoes, you might find yourself in a delightful tomato frenzy in late summer, only to face a dry spell in winter. This is where understanding the local growing seasons becomes crucial. It encourages us to adapt our diets to the natural cycles of our environment, which can be a rewarding experience.
Communities can support local farmers by embracing this seasonality. Here are a few ideas on how to do this:
- Seasonal Eating: Consider planning your meals around what is in season. Not only does this support local agriculture, but it also allows you to enjoy foods at their peak flavor and nutrition.
- Community Supported Agriculture (CSA): Joining a CSA can provide you with a regular supply of seasonal produce, helping you discover new fruits and vegetables while supporting local farmers.
- Farmers’ Markets: Visiting farmers' markets throughout the year can give you insight into what’s in season and help you connect with local growers.
Moreover, some local farms are becoming innovative by using techniques like hoop houses and high tunnels, which allow them to extend their growing seasons. This means that while you might not have access to certain crops in winter, you might still find fresh greens or root vegetables available. It's a testament to the resilience and creativity of local farmers who strive to meet community needs.
In summary, while the seasonal availability of local produce can present challenges, it also invites us to rethink our relationship with food. By embracing the seasons, we not only support our local farmers but also enjoy the freshest, most flavorful produce available. So next time you visit a farmers' market or a local farm, take a moment to appreciate the bounty of the season and the hard work that goes into bringing it to your table.
- What is seasonal produce? Seasonal produce refers to fruits and vegetables that are grown and harvested during specific times of the year based on climate and growing conditions.
- How can I find out what is in season? You can check local agricultural extension websites, farmers' markets, or community-supported agriculture programs to learn about seasonal produce in your area.
- Are there benefits to eating seasonal produce? Yes! Seasonal produce is often fresher, more nutritious, and supports local farmers and economies.

Competition with Industrial Agriculture
Local farmers often find themselves in a tough spot when it comes to competing with industrial agriculture. This behemoth of a sector benefits from economies of scale, allowing them to produce food at a fraction of the cost that local farms can manage. Have you ever wondered why a tomato from a supermarket can be so cheap? It’s likely because it has traveled thousands of miles from large-scale farms that are designed for mass production. In contrast, local farmers focus on quality and sustainability, which can sometimes lead to higher prices for their produce. But is it really fair to compare?
One of the main challenges local farmers face is the ability to keep up with the sheer volume and low prices of industrially produced food. These large farms often utilize advanced technology and extensive resources, which can create a significant gap in the market. Additionally, they have the advantage of distribution networks that allow them to reach consumers quickly and efficiently. This means that local farmers must find ways to differentiate their products and create a compelling value proposition for consumers.
To better understand this competition, let’s break down some of the critical factors at play:
| Factor | Local Agriculture | Industrial Agriculture |
|---|---|---|
| Production Scale | Small to medium scale | Large scale |
| Cost of Production | Higher due to sustainable practices | Lower due to economies of scale |
| Quality | Often fresher and organic | May use preservatives and chemicals |
| Distribution | Local markets and direct sales | Widespread distribution networks |
Despite these challenges, there is hope. Consumer awareness is on the rise, and more people are beginning to understand the importance of supporting local farmers. They recognize that purchasing local produce not only contributes to the local economy but also promotes environmental sustainability. As a result, local farmers can leverage this growing interest to carve out a niche in the market.
Moreover, policy changes can play a crucial role in leveling the playing field. If local farmers receive support through subsidies, grants, or favorable regulations, they can better compete with industrial agriculture. Communities can advocate for policies that prioritize local food systems, which can help create a more balanced market where both local and industrial agriculture can coexist.
Ultimately, the competition with industrial agriculture is a complex issue, but it is not insurmountable. By focusing on quality, sustainability, and community engagement, local farmers can thrive even in the face of significant challenges. So, the next time you’re at a farmers' market, remember that your support can make a world of difference not just for the farmer, but for the entire community.
- What are the main advantages of buying local food? Buying local food supports the economy, reduces carbon footprints, and often provides fresher produce.
- How can local farmers compete with large agricultural companies? By focusing on quality, sustainability, and community engagement, and by advocating for supportive policies.
- What role does consumer awareness play in supporting local agriculture? Increased consumer awareness can drive demand for local products, encouraging more people to buy from local farmers.

Strategies for Promoting Local Food Systems
Promoting local food systems is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for fostering sustainable communities and healthier lifestyles. To truly make an impact, we need to adopt effective strategies that encourage local agriculture and support our farmers. One of the best approaches is to engage the community actively. This means organizing events like local food festivals, farm tours, and cooking classes that spotlight the benefits of eating locally. When people see where their food comes from and learn how to prepare it, they become more invested in supporting local producers.
Another critical strategy is policy advocacy. Local governments can play a significant role in facilitating the growth of local food systems through supportive legislation. For instance, policies that provide grants or subsidies to local farmers can help them compete with larger industrial farms. Additionally, zoning laws can be adjusted to allow for urban farming initiatives, which can bring fresh produce right into our neighborhoods.
Moreover, we can’t overlook the importance of consumer education. Many people simply don’t know about the local options available to them. By utilizing social media, community bulletins, and local newsletters, we can spread the word about farmers' markets, community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, and seasonal produce. When consumers are informed, they are more likely to make choices that benefit local economies.
Here are some specific strategies to consider:
- Community Engagement Initiatives: Establish programs that invite community members to participate in local farming efforts, such as volunteer days at farms or community gardens.
- Support Local Markets: Encourage the establishment of farmers' markets and pop-up markets in neighborhoods to make local food more accessible.
- Education Workshops: Host workshops on topics such as gardening, cooking with seasonal produce, and understanding the benefits of local food.
Lastly, fostering partnerships between local businesses and farmers can create a win-win situation. Restaurants can feature local ingredients on their menus, while grocery stores can dedicate sections to local products. This not only supports farmers but also attracts customers who are eager to support their community.
In conclusion, promoting local food systems requires a multifaceted approach that combines community engagement, policy changes, consumer education, and business partnerships. By working together, we can create a thriving local food ecosystem that nourishes both our bodies and our communities.
Q: What are the main benefits of local food systems?
A: Local food systems reduce carbon footprints, support local economies, enhance food security, and provide fresher, more nutritious food options.
Q: How can I find local food sources in my area?
A: You can search for local farmers' markets, community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, and farm-to-table restaurants in your community. Social media and local government websites often have resources available.
Q: Are local foods more expensive than imported foods?
A: While some local foods may be pricier due to smaller scale production, many local options can be competitive in price, especially when considering the reduced transportation costs and the freshness factor.
Q: How can I support local farmers?
A: You can support local farmers by purchasing their products directly at farmers' markets, joining a CSA, and advocating for local agriculture policies.

Community Engagement Initiatives
Community engagement is the lifeblood of successful local food systems. When individuals come together, magic happens! Imagine a vibrant space where local farmers, consumers, and advocates unite to share knowledge, resources, and passion for sustainable food production. This collective effort not only strengthens local economies but also fosters a sense of belonging in the community. So, what are some effective ways to engage the community in local food initiatives?
One of the most impactful strategies is organizing community workshops. These workshops can cover a variety of topics, from organic gardening techniques to cooking classes that highlight seasonal produce. By providing hands-on experiences, community members can gain valuable skills while building relationships with local farmers. Furthermore, these workshops can serve as a platform for sharing stories and traditional cooking methods, creating a rich tapestry of culinary heritage.
Another essential initiative is the establishment of community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs. In a CSA, community members subscribe to receive regular shares of fresh produce directly from local farms. This not only ensures a steady income for farmers but also deepens the connection between consumers and their food sources. It’s like a box of surprises every week, filled with the freshest goodies, and it encourages families to explore new recipes and cooking techniques!
Moreover, organizing farmers' markets is a fantastic way to engage the community. These markets are more than just a place to buy food; they are a gathering spot where people can connect, learn about local agriculture, and support their neighbors. Farmers’ markets often feature live music, cooking demonstrations, and educational booths, making them lively hubs of community interaction. Imagine strolling through a market, chatting with the farmer who grew your tomatoes, and discovering the story behind your food!
To further enhance community engagement, local governments and organizations can implement advocacy programs aimed at promoting local food systems. By encouraging community members to voice their support for local agriculture, they can influence policy changes that benefit farmers and consumers alike. This could involve organizing letter-writing campaigns, public forums, or even social media initiatives to raise awareness about the importance of local food production.
In conclusion, community engagement initiatives are crucial for nurturing local food systems. By fostering connections among farmers, consumers, and local organizations, we can create a thriving ecosystem that benefits everyone involved. Whether through workshops, CSAs, farmers' markets, or advocacy efforts, every small action contributes to a larger movement towards sustainability and community well-being. So, let’s roll up our sleeves and get involved!
- What is community-supported agriculture (CSA)?
CSA is a system where consumers subscribe to receive shares of fresh produce directly from local farms, promoting a closer connection between farmers and consumers.
- How can I get involved in local food initiatives?
You can participate by attending workshops, shopping at farmers' markets, or joining a CSA program in your area.
- What are the benefits of engaging with local farmers?
Engaging with local farmers helps support the local economy, increases access to fresh produce, and fosters a sense of community.
- How do community workshops benefit participants?
Workshops provide hands-on experiences, teach valuable skills, and create opportunities for social interaction and learning.

Policy Advocacy for Local Agriculture
Advocating for policies that support local agriculture is essential for the sustainability and growth of local food systems. These policies can create an environment where local farmers thrive, ensuring that communities have access to fresh, nutritious food. But what does effective policy advocacy look like? It involves a combination of grassroots movements, collaboration with local government, and education about the benefits of local food production.
One of the most impactful strategies is to engage local communities in the advocacy process. When residents understand the importance of supporting local farmers, they are more likely to voice their opinions to policymakers. This can be achieved through community meetings, workshops, and social media campaigns that highlight the benefits of local agriculture. For instance, sharing success stories of local farms can inspire others to take action and support similar initiatives.
Moreover, it's crucial to establish strong relationships with local government officials. By presenting data and evidence that demonstrate the economic, environmental, and health benefits of local food systems, advocates can persuade policymakers to prioritize local agriculture in their agendas. This can include funding for local farms, subsidies for organic practices, or even zoning laws that favor small-scale farming.
Additionally, education plays a vital role in policy advocacy. Many consumers are unaware of the challenges that local farmers face, such as competition from industrial agriculture and the impact of climate change. By educating the public, advocates can foster a sense of urgency and responsibility among consumers, encouraging them to support policies that benefit local farmers. For example, campaigns can inform consumers about the importance of buying local produce and how it contributes to the economy and environment.
To further illustrate the significance of policy advocacy, consider the following table that outlines key policy initiatives that can support local agriculture:
| Policy Initiative | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Local Farm Subsidies | Financial support for local farmers to encourage sustainable practices. | Increased production and lower prices for consumers. |
| Zoning Reforms | Adjustments to land use regulations to support small-scale farming. | More opportunities for urban agriculture and community gardens. |
| Farm-to-School Programs | Partnerships between local farms and schools to supply fresh produce. | Improved nutrition for students and support for local farmers. |
In conclusion, policy advocacy for local agriculture is a multifaceted approach that requires community engagement, education, and strong relationships with policymakers. By working together, communities can create a supportive environment for local farmers, ensuring that everyone benefits from the bounty of locally grown food. As we move forward, it is essential to keep the momentum going and continue to advocate for policies that prioritize local agriculture for a sustainable future.
Q1: What are the benefits of supporting local agriculture?
A1: Supporting local agriculture helps reduce carbon footprints, boosts the local economy, and provides fresher, healthier food options.
Q2: How can I get involved in local food advocacy?
A2: You can participate in community meetings, support local farmers' markets, and advocate for policies that benefit local agriculture.
Q3: Are there financial incentives for local farmers?
A3: Yes, many local governments offer subsidies and grants to support sustainable farming practices and local food initiatives.
Q4: What challenges do local farmers face?
A4: Local farmers often contend with competition from industrial agriculture, seasonal availability of produce, and limited access to markets.

Conclusion: The Future of Local Food Production
As we look ahead, the future of local food production appears to be a bright and promising path toward achieving sustainability and enhancing community health. The benefits of sourcing food locally extend beyond just the plate; they ripple through our economies, our environments, and our social structures. Imagine walking through a vibrant farmers' market, where the air is filled with the aroma of fresh produce, and the community buzzes with conversations about food and health. This is not just a dream—it's a reality we can cultivate.
By prioritizing local food systems, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprints, support local farmers, and foster a sense of community. The potential for economic resilience is immense; when we invest in local agriculture, we create jobs and keep money circulating within our communities. It's like planting seeds that will grow into a sustainable future, providing nourishment not just for our bodies, but for our economy as well.
However, realizing this vision requires collective effort. From consumers to policymakers, everyone has a role to play in promoting local food initiatives. We need to advocate for policies that support local farmers and educate ourselves about the importance of eating locally. By doing so, we can create a robust system that not only sustains us but also thrives in the face of global challenges.
Ultimately, the future of local food production hinges on our willingness to embrace change and support our local systems. Together, we can forge a path that leads to healthier communities and a healthier planet. The question we must ask ourselves is: are we ready to invest in our future through the food we consume? Let's take that leap and champion local food production for the generations to come.
- What are the main benefits of local food production?
Local food production reduces carbon emissions, supports the local economy, and enhances community health. - How can I support local farmers?
Shop at farmers' markets, join community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, and advocate for local food policies. - Are there challenges to local food production?
Yes, challenges include seasonality, competition with industrial agriculture, and scalability. - How does local food impact nutrition?
Local food is often fresher and more nutrient-dense, leading to better health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the environmental benefits of local food production?
Local food production can significantly reduce carbon footprints by minimizing transportation distances. This means fewer greenhouse gas emissions, which is a big win for our planet! When you buy food grown nearby, you're not just getting fresher produce; you're also helping the environment by promoting ecological balance.
- How does supporting local farmers boost the economy?
Investing in local food systems creates jobs and enhances economic resilience. When you support local farmers, you're helping to keep money within your community. This not only creates employment opportunities in farming and distribution but also strengthens the local economy against global market fluctuations.
- What health benefits come from consuming local foods?
Eating locally produced foods can lead to improved health outcomes. Local foods are often fresher and more nutrient-dense than mass-produced alternatives. The shorter time from farm to table means you get to enjoy fruits and vegetables at their peak freshness, which is great for your health!
- Are there challenges associated with local food production?
Yes, local food production faces several challenges, such as seasonal availability and competition with industrial agriculture. Seasonal changes can limit the types of produce available at different times of the year, and local farmers often struggle against the lower prices and larger scale of industrial farms.
- What strategies can help promote local food systems?
Effective strategies for promoting local food systems include community engagement initiatives and policy advocacy. Encouraging participation in local agriculture and advocating for supportive policies can help create a more sustainable and resilient local food network.
- How can community members get involved in local food initiatives?
Community members can get involved by shopping at farmers' markets, participating in community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, or volunteering at local farms. Every little effort counts towards building a stronger local food system!



















